Data Warehousing
Data Warehousing is the process of taking data from legacy and transaction database systems and transforming it into organized information in a user-friendly format to encourage data analysis and support fact-based business decision making.
A data warehouse is a system that extracts, cleans, conforms, and delivers source data into a dimensional data store and then supports and implements querying and analysis for the purpose of decision making.
From your data warehouse, data cubes are tables/files which index and precompute desired data results. In your cube you could have all those precomputed values: sales by months, by week, by salesman, by client, by geographical region, by product color, etc. Then you can run OLAP queries on your cube to have the total, average and maximum sales by (month, salesman, region), or by (color, region), or by (salesman, month). Since all the data is precomputed and indexed, the queries are really fast.
The Data Warehouses have to be activated via the Daily Systems Snapshot and Inventory Data Warehouse Options .
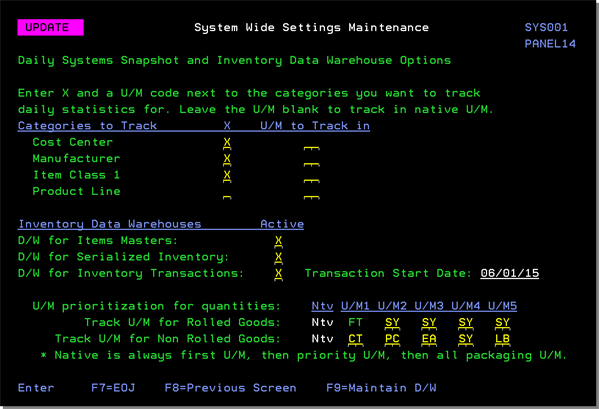
The Transaction Start Date determines the records written and updated in the file via the transaction date. The records written must have a transaction date greater than or equal to the start date setting.
The U/M prioritization for quantities is primarily for the Serialized Inventory data warehouse. This allows for a distinct unit of measure to always be in the same column for easier analysis. If a unit of measure entered is invalid for a particular item, the column will still be present in the file and export, but will have a zero value.
Enter up to 5 U/Ms for both Rolled and Non Rolled goods.
F9 = Maintain D/W (Data Warehouse)
This option displays the following options.
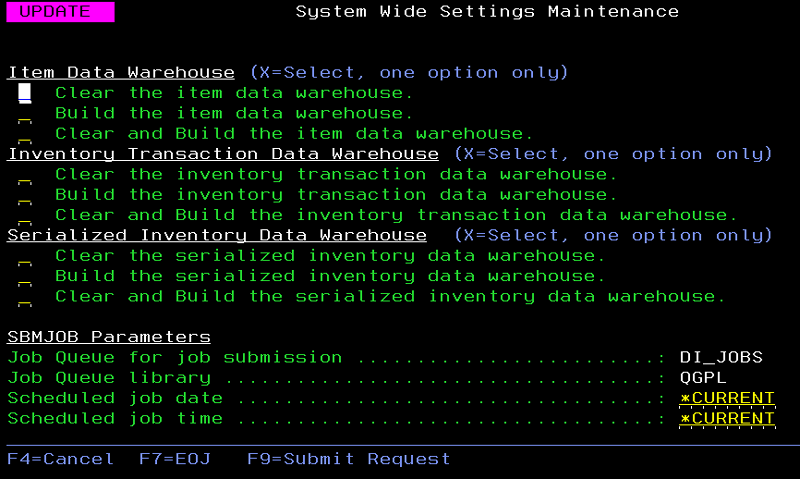
- Job Queue for job submission / Job Queue library - Provide a place for the job queue and library of the job queue for the user to submit the job into. The Job Queue will always be set to DI_JOBS (to avoid blocking QBATCH).
- Scheduled job date / Scheduled job time - Provides a date and time for the submitted job to run. This allow the user to preschedule the job to run off regular business hours. It will adjust the Schedule Date/Time on the SBMJOB command. The default is *CURRENT.
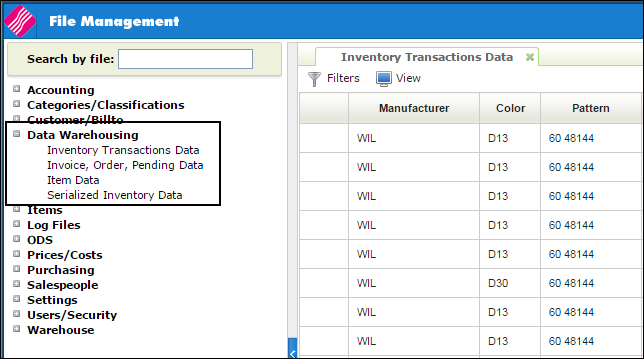
Data Warehouses are accessible via the Navigator File Management application.
This data warehouse shows all inventory activity such as quantity and date of the transaction, the value of the transaction and the initials of the operator performing the transaction. It also shows all the units of measure in the Packaging File.
This data warehouse pulls information from the Open Inventory, Item, Manufacturer, Supplier, Stock Keeping Unit (SKU) files, inventory adjustments and receipts, customer orders, purchase orders and invoices.
Click here to see the file layout for the Inventory Transaction Data Warehouse.
Add Fields to the Data Warehouse File for Orders and Invoices
You can use this data warehouse to show customer order, purchase order and/or invoice information.
Information is pulled from the Open Order, Pending Order, and Invoice Files.
This database file is populated from database triggers on the PENDING, OPENPO, and INVOICE files.
Records are written to the database with a D1TYPE of P when they are entered into Order Entry and are added to the PENDING file. Once an order is processed, the D1TYPE becomes O and the record is updated with the OPENPO values of data. When the order is invoiced, the D1TYPE becomes ‘I' and the record is updated with the INVOICE values of data.
Because the file is based on database triggers, the contents of the data is always recalculated in real time to have the current values of the associated workflow.
Click here to see the field layout in this database.
When looking at the field layout via the hyperlink above, you will see there are three types of records.
- A – Alpha - alpha is all characters
- S - Signed - signed is numeric where the length of the field is the number of digits and decimals.
- P - Packed - A packed decimal representation stores decimal digits in each nibble of a byte. Each byte has two nibbles, and each nibble is indicated by a hexadecimal digit. For example, the value 15 is stored in two nibbles, using the hexadecimal digits 1 and 5. Packed takes up half the space because the numbers are stored in each nibble, which is why we shod the start and end positions, because you will notice the length of the data field for packed is about half of the length of the from/to positions.
This information comes from the Item File (menu option FIL 2 on the green screen or the Item file in the Navigator File Management application). Keep in mind, it pulls information from every part of the Item File.
Information is also pulled from the Manufacturer, Supplier and IWMS applications.
Click here to see the file layout.
This option allows you to extract serialized inventory data for internal data analysis. The information in this data warehouse is pulled in from the Item, Inventory, and Manufacturer, Stock Keeping Units (SKU) and Supplier files. Includes serial number level information at the native unit of measure and all units of measure in the Packaging File.
Click here to see the file layout.
This Data Warehouse contains all the native packaging factors for the item masters, which use a packaging class.
Updating the Item Packaging Data Warehouse
Assigning Packaging Classes
Packaging classes are assigned to items via the Item File (FIL 2).
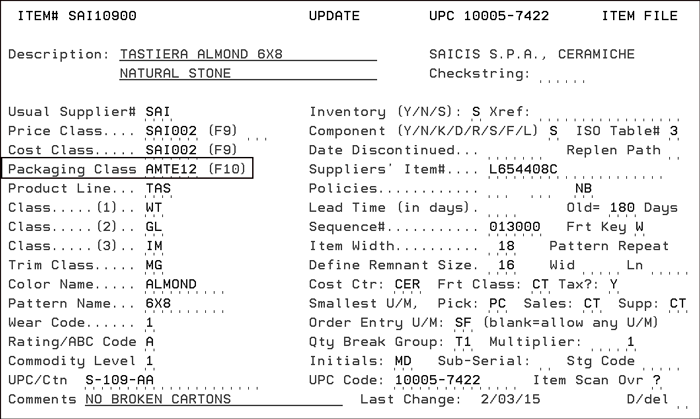
Packaging Classes are created and maintained via the Packaging Class file (FIL 13).
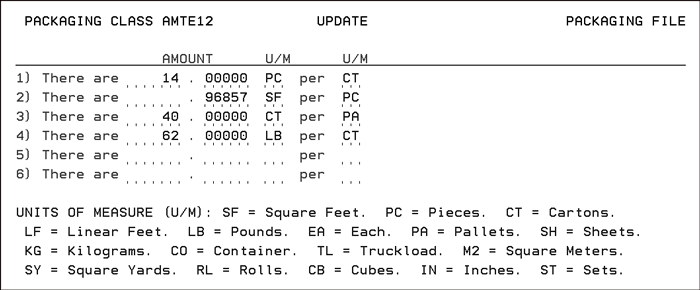
Updating the Item Packaging Data Warehouse
This Data Warehouse is updated when the Build Item Packaging Extracted (menu option 614) is run.
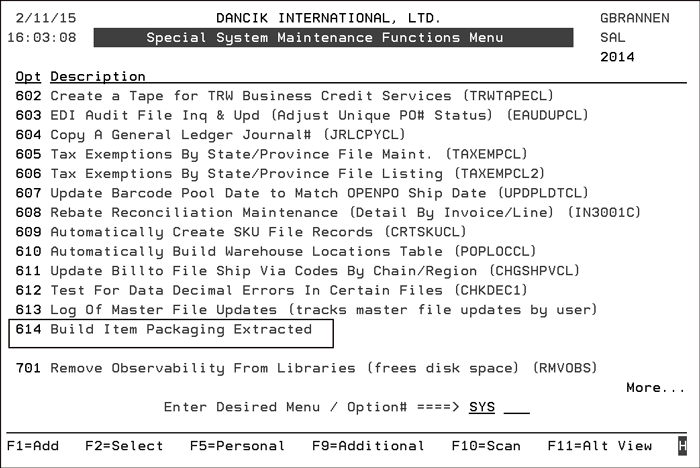
An example of the Extract is shown below.

Field Layout
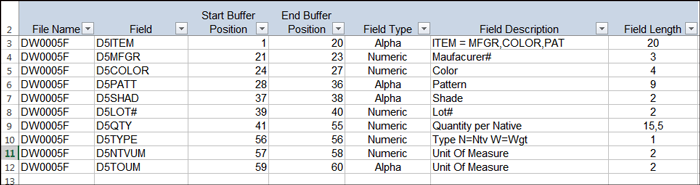
All four of these data warehouses pull in a lot of information from several different files. You can use the filters to narrow the results displayed as needed.
The use of these filters to narrow the information pulled is strongly encouraged. If the filters are not used, the data sets could be extremely large.
When you first access one of the data warehouses, a filter screen appears. Use it to select the information you need.
The information displayed in every data warehouse can be exported to an Excel spreadsheet via the icon in the upper right hand corner.